Selecting the right cookware can be a daunting task, given the myriad of options available in the market. From different materials to various types and sizes, the choices can be overwhelming. This guide will help you navigate through the essential factors to consider when choosing cookware, ensuring you make informed decisions that enhance your cooking experience.

1. Material Matters Cookware
The material of your cookware affects its performance, durability, and maintenance. Here are some common materials and their properties:
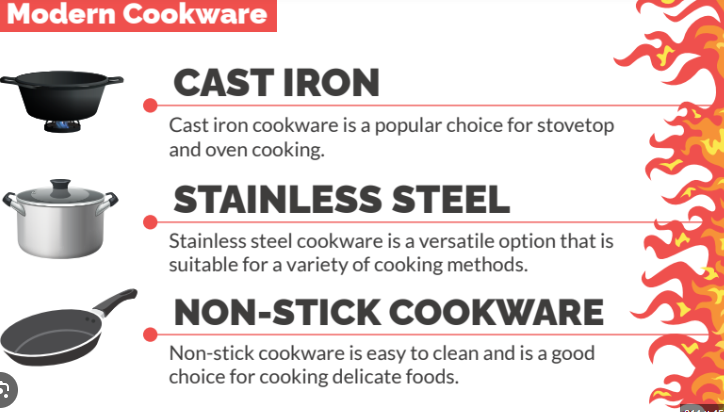
Stainless Steel
- Pros: Durable, non-reactive, and easy to clean.
- Cons: Poor heat conductivity (unless combined with aluminum or copper).
Non-Stick
- Pros: Easy to clean and great for low-fat cooking.
- Cons: Can be scratched easily; needs to be replaced more frequently.
Cast Iron
- Pros: Excellent heat retention, versatile (can be used on stovetops and in ovens), and can develop a natural non-stick surface.
- Cons: Heavy and requires maintenance to prevent rust.
Copper
- Pros: Superior heat conductivity and precise temperature control.
- Cons: Expensive and requires regular polishing.
Aluminum
- Pros: Good heat conductivity and lightweight.
- Cons: Can react with acidic foods, often needs to be anodized or clad with other materials.
2. Types of Cookware
Different types of cookware serve various purposes. Here’s a breakdown of essential pieces:
Saucepan
- Ideal for making sauces, boiling pasta, and reheating soups.
- Look for a heavy bottom to prevent scorching.
Frying Pan/Skillet
- Perfect for frying, sautéing, and browning.
- Non-stick options are great for eggs and pancakes, while stainless steel or cast iron is better for searing meats.
Stockpot
- Used for making soups, stews, and boiling large quantities of food.
- A larger size (8-12 quarts) is versatile for most cooking needs.
Dutch Oven
- Excellent for slow-cooking, braising, and baking.
- Cast iron Dutch ovens are popular for their even heat distribution and retention.
Sauté Pan
- Similar to a frying pan but with higher sides.
- Great for sautéing, searing, and reducing sauces.
3. Heat Conductivity and Retention

Good heat conductivity ensures even cooking, while heat retention keeps your food warm. Copper and aluminum offer excellent heat conductivity, while cast iron excels in heat retention. Stainless steel with an aluminum or copper core provides a good balance.
4. Ease of Maintenance
Consider how much effort you’re willing to put into maintaining your cookware:
- Non-stick pans need gentle cleaning and should avoid metal utensils to prevent scratching.
- Cast iron requires seasoning and careful drying to prevent rust.
- Stainless steel is generally dishwasher safe and easy to clean.
5. Compatibility with Cooktop
Ensure your cookware is compatible with your cooktop:
- Induction cooktops require magnetic cookware (e.g., stainless steel, cast iron).
- Gas and electric cooktops are generally compatible with most types of cookware.
6. Size and Quantity
Consider the size and quantity of cookware based on your cooking habits and family size:
- A small family might need fewer, more versatile pieces.
- Larger families or avid cooks might benefit from a more extensive set.
7. Budget Considerations
While high-quality cookware can be a significant investment, it often pays off in the long run. Prioritize essential pieces and materials that suit your cooking style and gradually build your collection.
8. Additional Features
Look for additional features that enhance usability:
- Oven-Safe Handles: Allow for seamless stovetop-to-oven cooking.
- Tempered Glass Lids: Enable you to monitor cooking without lifting the lid.
- Riveted Handles: Provide extra durability.
Conclusion
Choosing the right cookware involves balancing material properties, types, maintenance, compatibility, and budget. By understanding the various options and what suits your cooking style best, you can build a cookware collection that not only meets your needs but also enhances your culinary adventures. Happy cooking!

